When Xiao Hao was three years old, his mother found that his bones became more and more "hard": he couldn’t squat, his arms were difficult to bend, and he was accompanied by hepatosplenomegaly and heart reflux. Sadly, he was never diagnosed … …

After six years, Xiao Hao was finally diagnosed — — Suffering from mucopolysaccharide storage type ⅱ, thus, a family knows that there is such a rare disease in the world.
May 15th every year is the International Care Day for Mucopolysaccharide Storage. When children have symptoms such as rough face, stunted growth, thick joints, big head, "chicken breast", hepatosplenomegaly, abnormal heart and even mental retardation, they must be careful of Mucopolysaccharide Storage. Mucopolysaccharide, also known as glycosaminoglycan, is a macromolecular substance widely existing in human cells. Mucopolysaccharide is a big family. Your skin is white and tender, your joints are flexible, and your eyes are bright, which is closely related to the members of the "Mucopolysaccharide" family.
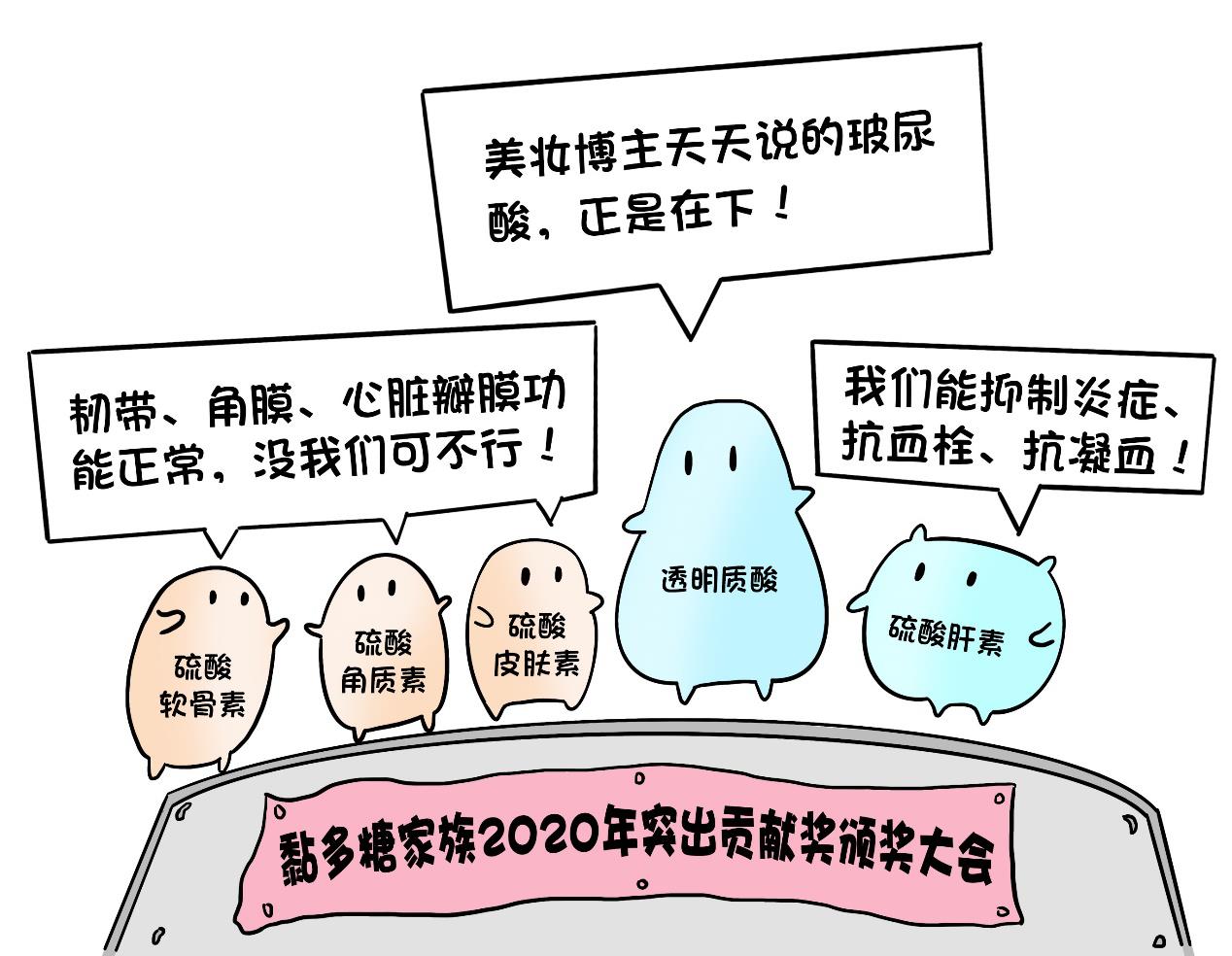
Although the mucopolysaccharide family is miraculous, there must be a premise that our cells can digest them normally, and the cells have specially prepared a "digestion workshop" — — Lysosome.
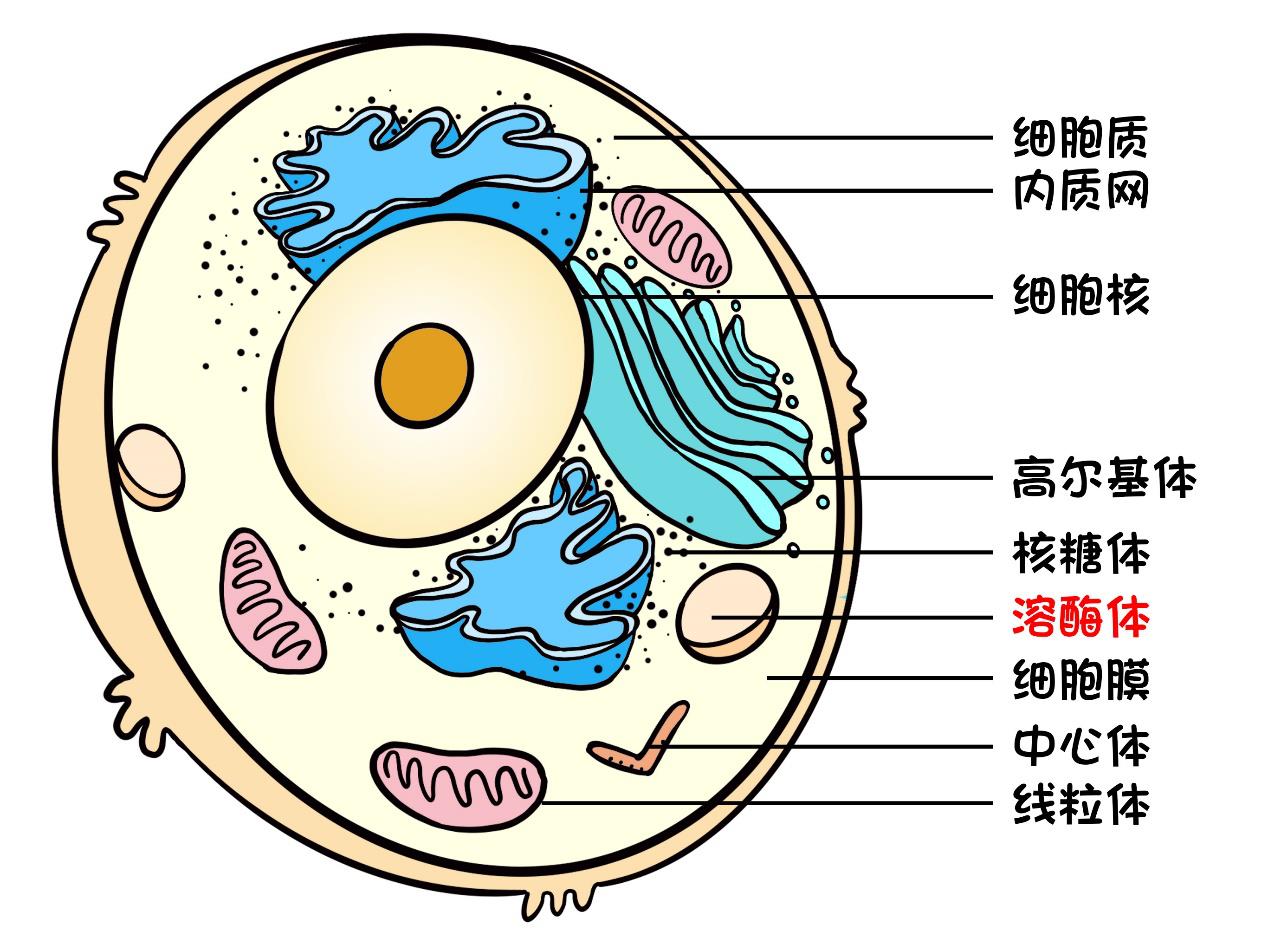
Lysosomes specialize in degrading foreign or endogenous biological macromolecules, such as lipids, glycogen and mucopolysaccharides, etc., and they can take this big job because of more than 60 enzymes contained in them.
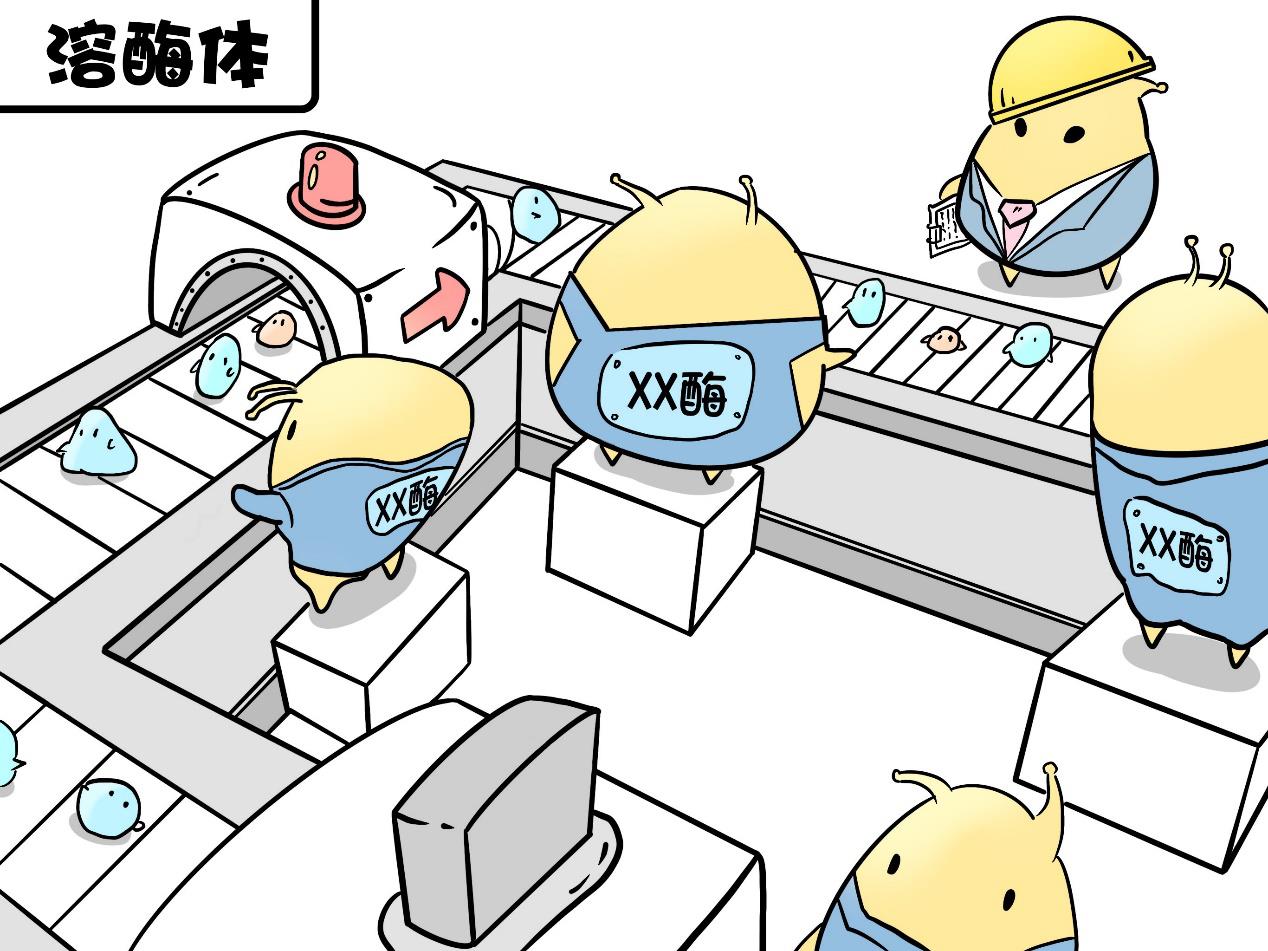
More than 60 kinds of enzymes have their own functions, without any one of them, a specific biological macromolecule may not be degraded normally, thus being stored in lysosomes.
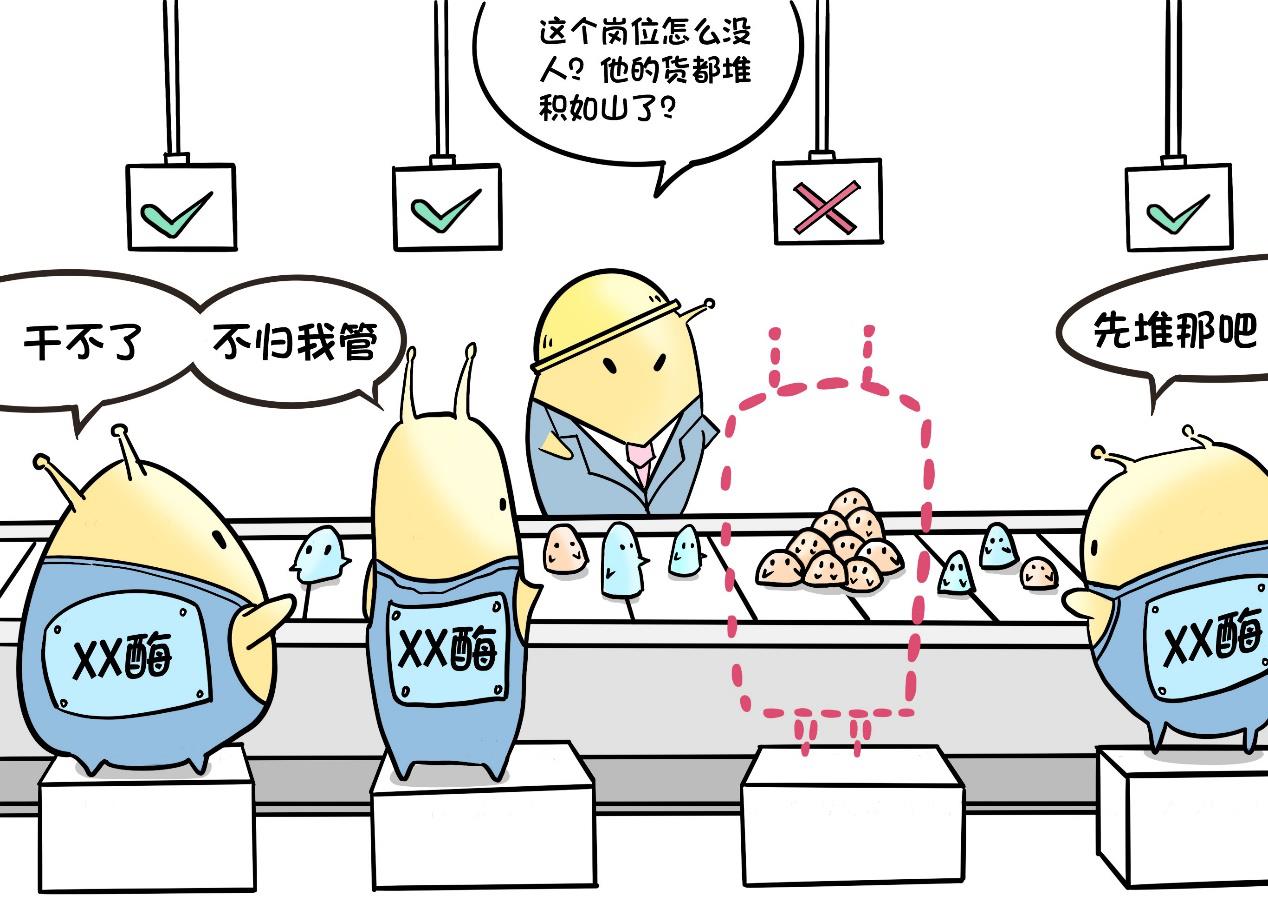
Lysosomes began to swell, eventually making cells bloated and abnormal, and indigestible macromolecules deposited in various organs of the body, and people’s symptoms became more and more obvious.
The reason of enzyme deficiency is often gene mutation. Mucopolysaccharide storage disease (MPS) is a congenital genetic and metabolic disease, which leads to the deposition of this kind of mucopolysaccharides because of the lack of enzymes that decompose the corresponding mucopolysaccharides.
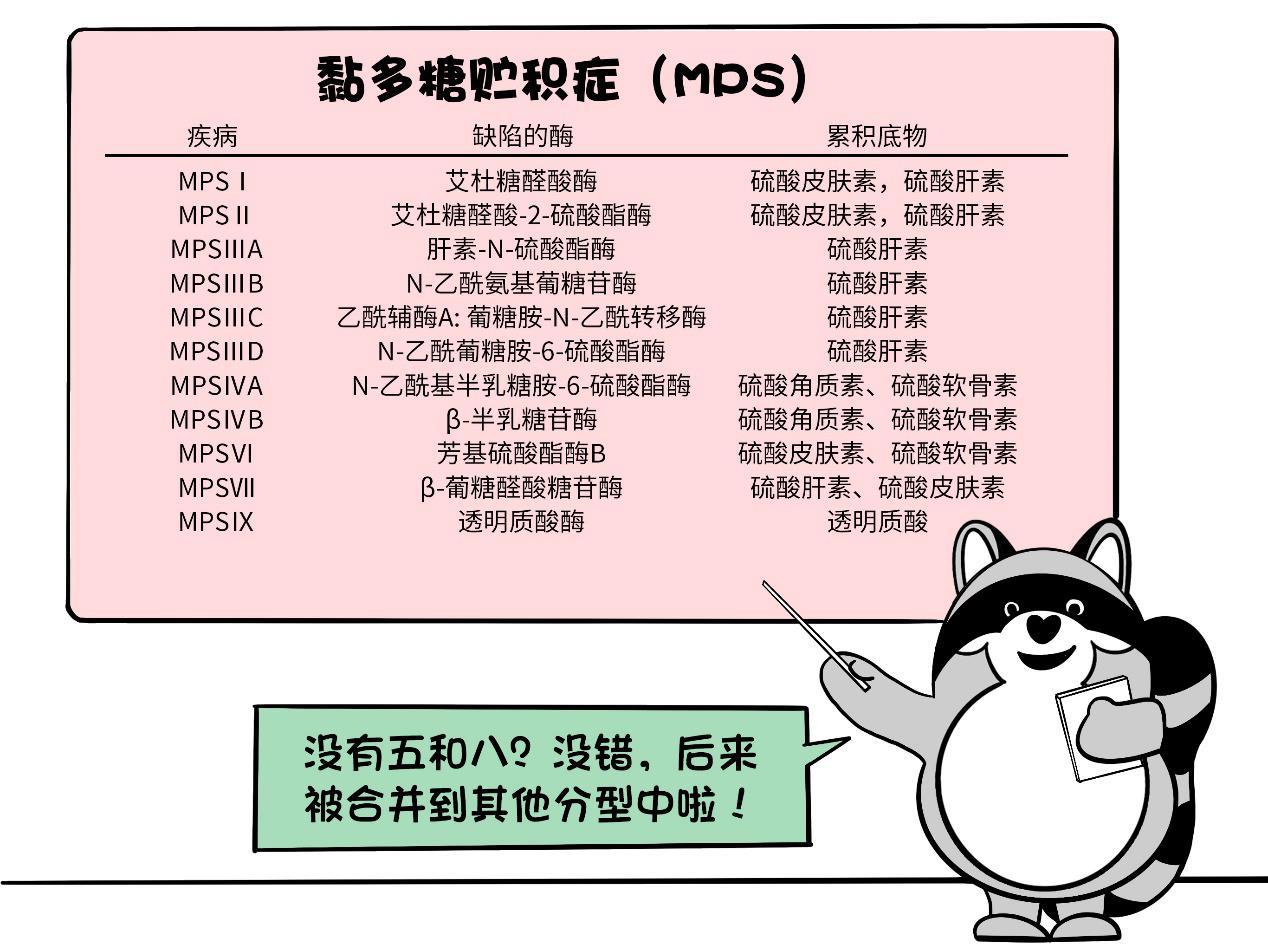
According to the different enzymes, mucopolysaccharide storage disease can be divided into seven types and multiple subtypes.
Although there are many types, MPS patients have some basic characteristics: multiple organs in the whole body are affected, the development is delayed, and the condition is gradually aggravated; Short stature, rough face, big forehead protrusion, skeletal deformity, thick joints, claw-shaped hands, corneal opacity, otitis media, narrow respiratory tract, hepatosplenomegaly, heart disease, and serious cases will affect intellectual development.
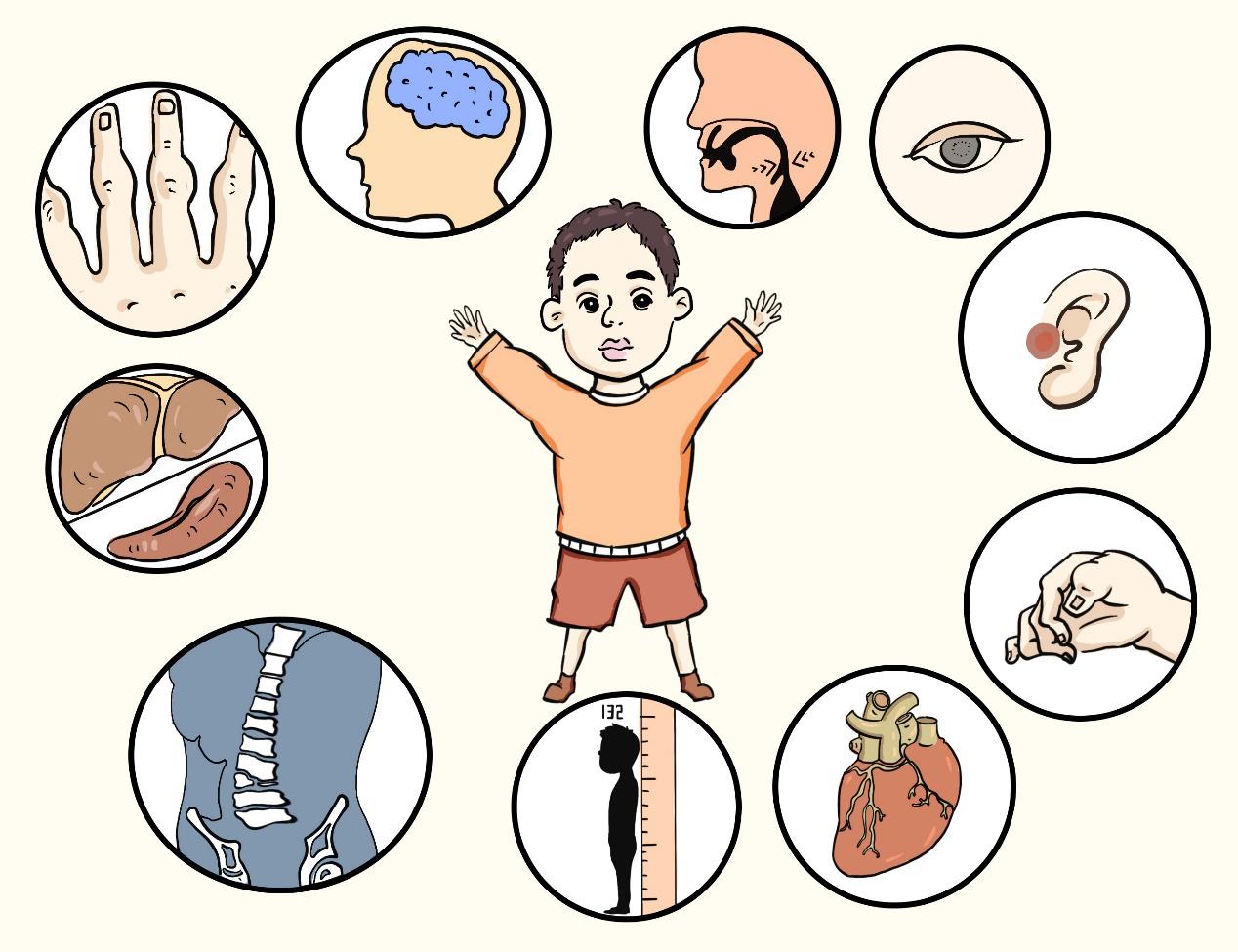
There are differences between different types. For example, the majority of patients with type II are men, patients with type III show obvious mental retrogression, and patients with type IV concentrate on skeletal deformity. Similarly, the disease has brought a heavy burden to every patient’s family.

Most of the patients with mucopolysaccharide storage disease are children, and they are affectionately called "sticky babies" in China, because the symptoms of MPS are complex and rare, and there may be many undiagnosed MPS patients who are struggling to seek medical treatment in confusion.

At first, there was no specific treatment for MPS, and only symptomatic treatment could relieve the pain. In recent years, enzyme replacement therapy has become an effective treatment for some MPS. Simply put, it is "what enzyme is lacking".
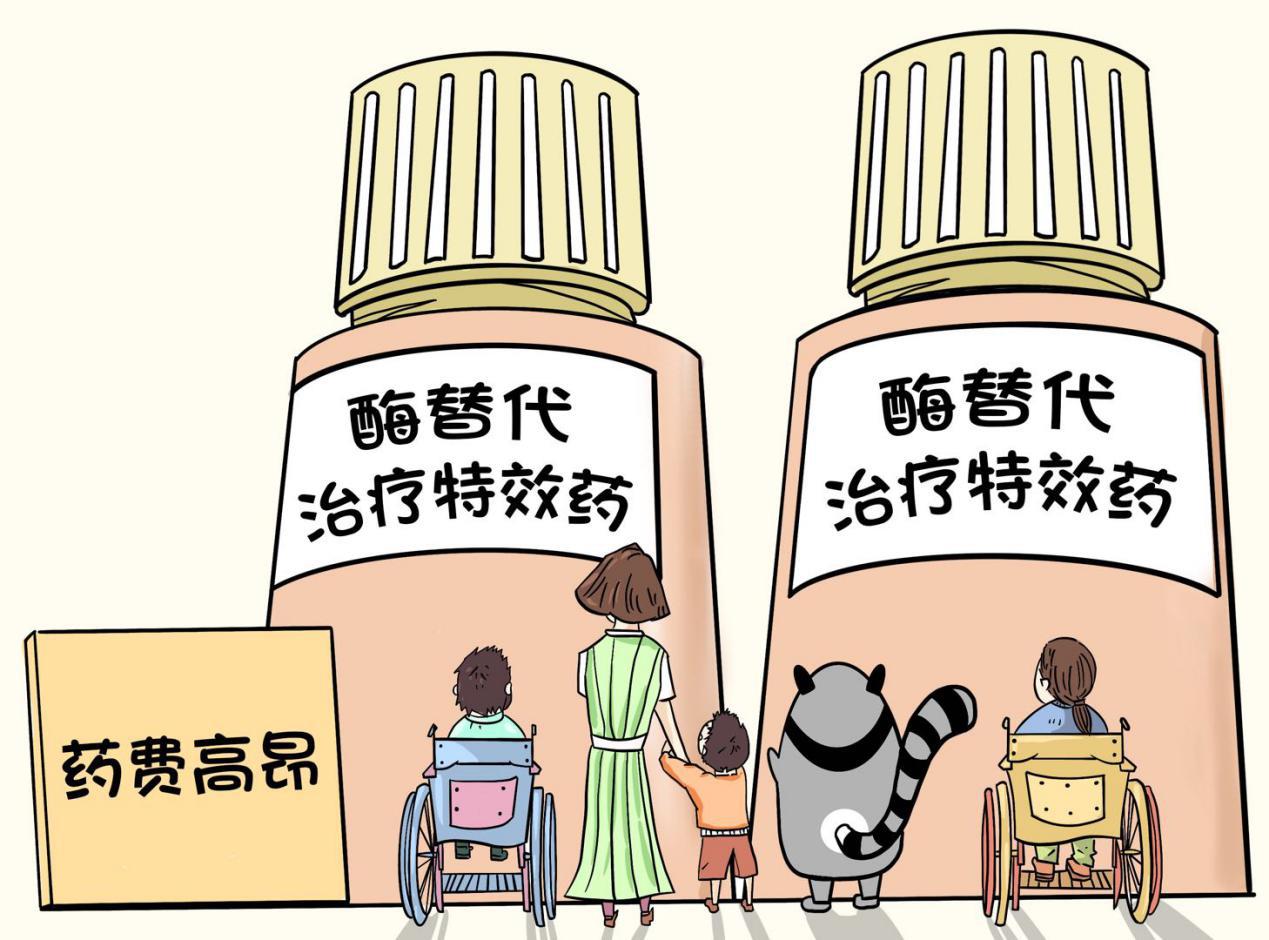
In recent years, with the country’s increasing attention to rare disease groups, the research and development or introduction of drugs for rare diseases is accelerating. At present, MPSⅣA has become the first MPS therapeutic drug approved for marketing in China. Type I and type II drugs are also expected to be listed in China soon. Type III drugs are still under development; However, as far as the drugs on the market are concerned, they are expensive. Without medical insurance, ordinary families will face an unbearable situation.
If we can use specific drugs from an early age, Sticky Baby can enjoy a high-quality life like us. Even if they can’t take medicine, there are still many MPS patients who insist on going to school or work actively, playing their own part.

May 15th every year is the International Care Day for Mucopolysaccharidosis. The MPS family in trouble needs everyone’s attention and support. Let’s join these lovely "sticky babies" and hope that the day when medicine can be used will come soon!


Medical Guidance: Chief Physician Zhang Huiwen
Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine
Shanghai Institute of Pediatric Medicine
Shanghai Children Rare Disease Treatment Center
References:
[1] Zhang Huiwen, Wang Yu, Jun Ye, Qiu Wenjuan, Han Lianshu, Gao Xiaolan, Gu Xuefan. Common enzymatic classification of 47 cases of mucopolysaccharide storage disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Pediatrics, 2009,47 (4): 276-280.
Shi Huiping. Case diagnosis and prenatal diagnosis of lysosomal storage disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Pediatrics, 1999,37 (1): 57-58.
Wu Xiru, Bao Xinhua. Progress in diagnosis and treatment of lysosomal storage disease [J]. Journal of Peking University (Medical Edition), 2005,37 (4): 440-444.
Tian Zhiqiang, Ji Shengli. Relationship between glycosaminoglycans and inflammation [J]. Chemistry of Life, 2005,25 (6): 485-487.
(Written by Hao Yu, Illustrator/Mai Chuan)